Listen
to this Fuel for Thought podcast.
Mainland China's transition to electrification reached a major
milestone in July 2024 when sales of new-energy vehicles (NEVs)
surpassed internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles for the first
time, according to data released by the China Passenger Car
Association (CPCA).
NEVs include battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid
vehicles (PHEVs) and range-extended electric vehicles (REEVs). In
2023, automakers' aggressive sales promotions and a tidal wave of
new model launches helped to boost sales of NEVs in mainland China
after the 2022 withdrawal of the central-government subsidy
programs.
It is beyond doubt that the Chinese auto market will continue to
transition to electric vehicles in the next few years with
automakers advancing their electrification plans. S&P Global
Mobility expects that NEV share of the Chinese passenger vehicle
market will reach 46% in 2024, compared to 36% in 2023.
The acceleration in the market's shift to EVs will be helped by
declining battery prices, a wider availability of models and the
intense level of competition that exists in the market.
With NEVs going mainstream, trends taking shape in the sector
have begun to affect the broader passenger car market and influence
consumer choices.
EV adoption increasingly driven by plug-in hybrid
models with BEV sales slowing down
Although purchases of BEVs, PHEVs and REEVs are all eligible for
the central-government's purchase tax reduction incentive programs
through 2027, what is really accelerating the market's shift to
electrification in 2024 are PHEVs and REEVs, rather than pure
electric vehicles.
In the first half of 2024, Chinese sales of BEVs rose by 12%
year over year to 3.02 million units, by comparison, sales of
PHEVs, including vehicles with extended-range electric powertrain,
surged by 85% year over year to 1.92 million units in the first
half of this year.
These market dynamics were already taking shape in 2023. S&P
Global Mobility research shows that combined sales volumes of PHEVs
and REEVs in the passenger vehicle market surged by 83% year over
year in 2023 to 2.75 million units, while that of BEVs grew by 20%
to 5.2 million units.
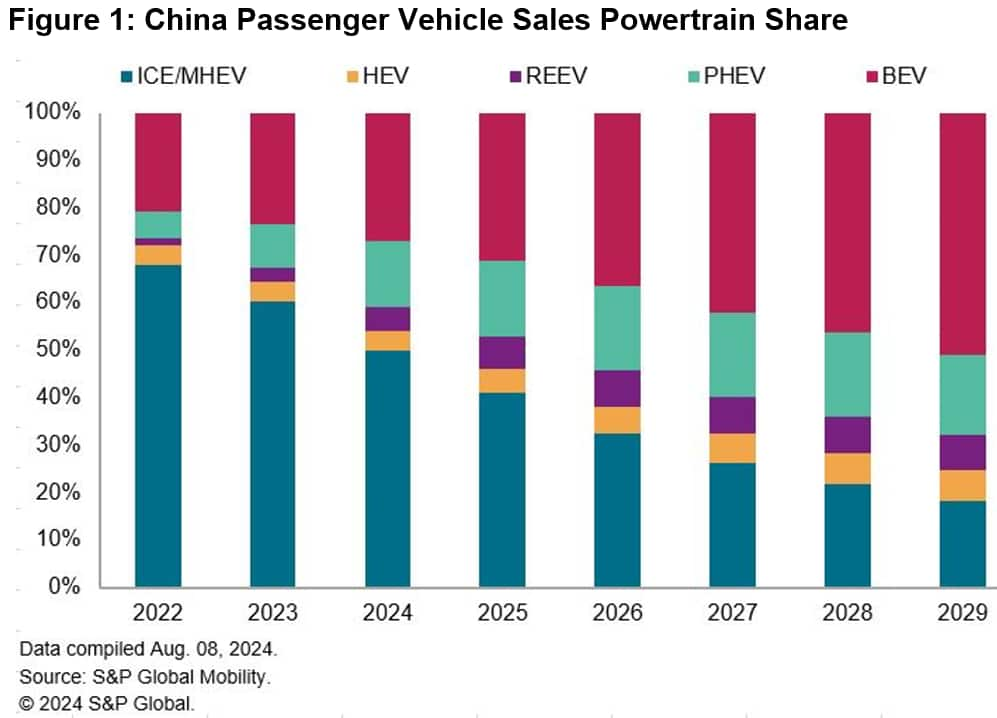
S&P Global Mobility expects PHEV and REEV sales in mainland
China to continue to grow in the next few years, accounting for 24%
of total passenger vehicle sales by 2029. Despite a slowdown in the
annual growth rate, BEV sales share is expected to reach 51% in
2029. Together, the total NEV sales share would be 75% that year,
according to S&P Global Mobility forecasts.
Growing presence of Chinese automakers poses a
challenge for global companies
Chinese brands' strong presence in the NEV market has helped
them to advance their market share in the overall passenger vehicle
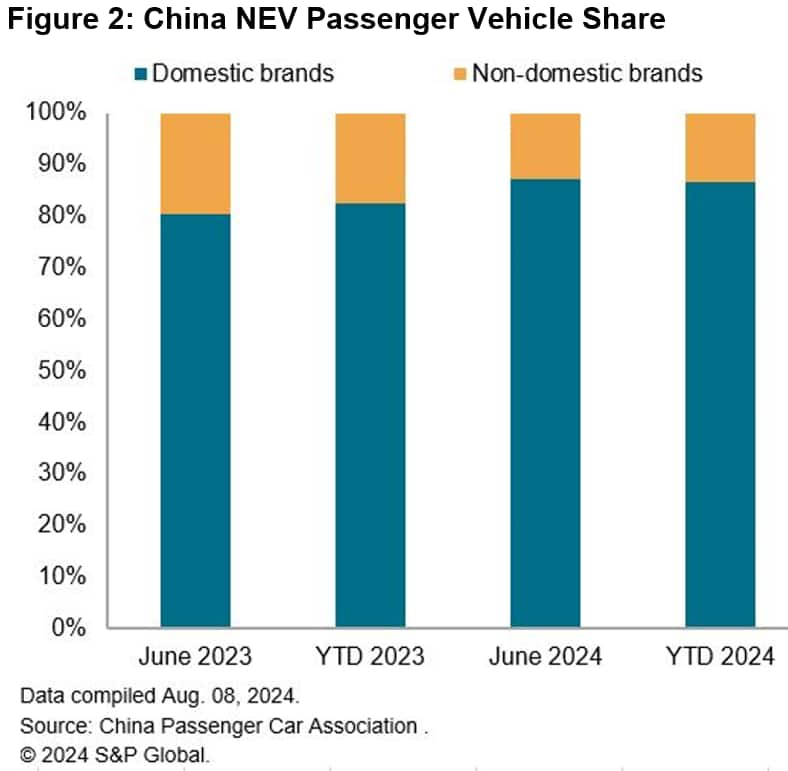
market. Domestic brands' market share in the Chinese retail
passenger NEV market increased from 83% in the first half of 2023
to 87% in the first half of 2024, while their global counterparts
have a combined sales share of less than 15% in the first six
months of 2024.
Chinese OEMs' growing presence in the NEV market has led to a
shift in consumer preferences over brands and models. Global OEMs,
especially the Japanese brands, have struggled to match their
Chinese rivals in the speed of adapting to changing consumer demand
and market conditions. Toyota has already cut production at its
Chinese JVs by 22% year over year in the first half of 2024 to cope
with declining demand. Nissan and Honda, the other two major
Japanese automakers in mainland China, have all recorded huge
declines in Chinese sales during 2024, faced with BYD's aggressive
product offensive.
In addition, the premium automakers, including the big 3 German
brands, also face the challenge of commanding a price premium for
their new-generation BEVs as price competition intensifies. To keep
up with the speed of innovation in China and reduce development
costs, VW is working with Xpeng and SAIC Motor on separate EV
programs that will use the two Chinese companies' vehicle platforms
and software technologies. VW's upcoming new launches in mainland
China will also include long-range PHEVs and REEVs developed
jointly with SAIC.
S&P Global Mobility's latest projection shows Chinese
brands' sales share in the country's passenger NEV market is set to
reach 87% in 2024, further improving from 83% in 2023. With global
automakers rolling out their new-generation BEVs and PHEVs in
mainland China in the next few years, we expect global brands'
market share to improve from 2026 onwards to reach 25% in 2029 with
VW and BMW contributing strongly.
Chinese tech companies tapping into consumer
preferences for SDVs
Software is increasingly a point of difference in influencing
buying choice in mainland China. Growing consumer interest in
software-defined vehicles (SDVs) presents an opportunity for
mainland China's tech companies to tap into the electric vehicle
market.
Xiaomi Corporation, a leading smart phone manufacturer, aims to
deliver 100,000 EVs this year. The company's first electric model,
the SU7 sedan, has received unprecedented publicity in mainland
China thanks to Xiaomi's strong brand appeal, its huge consumer
electronics products userbase and new smart car features it
introduced to the SU7.
China's telecom giant Huawei also emerged as a major player in
the NEV sector, providing a range of intelligent vehicle
technologies to its OEM partners. The success of AITO, a
Huawei-backed NEV brand, has encouraged China's state-backed
automakers including BAIC and JAC to forge partnerships with Huawei
to transition their product line with software-defined cars.
China's export surge met with new trade
barriers
Although electrification in mainland China continues to grow,
the country's status as an EV production and export hub may face
some challenges.
Mainland China's EV exports surged in the past two years amid
automakers' efforts to expand sales in global markets. Data from
the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) suggests
China's NEV exports reached 1.2 million units in 2023, compared
with less than 680,000 units in 2022.
Although Tesla contributed largely to mainland China's EV export
surge in recent years, growing EV shipment volumes of Chinese
automakers including SAIC and BYD has fueled concerns over China's
overcapacities and its intention to dominate the global market with
low-price vehicles.
The EU's provisional tariffs, which adds up to 36.3% of custom
duties to Chinese-built BEVs, are the latest example of rising
protectionist actions taken by major economies to protect their
market from the influx of BEVs originating in China. Canada and the
US have also announced strict tariffs on China-made BEVs.
Automakers are looking to cope with these trade barriers by
shifting production of certain models to other manufacturing
locations or investing in local production capacities to circumvent
tariffs. The high tariffs will also prompt automakers to further
optimize their cost structure to maintain a reasonable margin
level.
However, within the automotive sector, major global automakers
including Stellantis and Volkswagen are seeking their own way to
keep up with competition from Chinese rivals. Both automakers have
invested in Chinese EV startups in the past year to gain access to
EV know-hows—especially software architecture—and speed up
new launches. The Stellantis and Leapmotor joint venture already
began shipment of Leapmotor EVs built in mainland China to Europe
in July.
To cope with the EU tariffs, Stellantis also kicked off assembly
of the Leapmotor T03 EV at its plant in Poland from
semi-knocked-down kits imported from mainland China.
S&P Global Mobility offers detailed sales-based
powertrain forecasts for the United States, Canada, Brazil, United
Kingdom, Italy, Germany, France, Spain, Netherlands, Sweden,
Norway, Rest of EU30, India, mainland China, and Australia.